Cañadas O, Sáenz A, de Lorenzo A, Casals C.
Pulmonary surfactant inactivation by β-D-glucan and protective role of surfactant protein A.
Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021 Nov 21:112237
DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.112237
RESUMEN
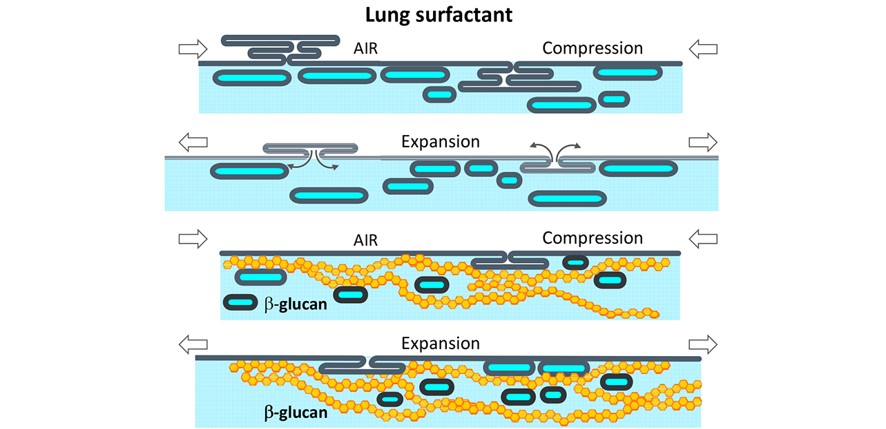
Pulmonary fungal infections lead to damage of the endogenous lung surfactant system. The objective of this study was to characterize the interaction of β-D-glucan, the major component of pathogenic fungal cell walls, with pulmonary surfactant. Our results show that β-D-glucan induced a concentration-dependent inhibition of the surface adsorption, respreading, and surface tension-lowering activity of surfactant preparations containing surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C. Our data support a new mechanism of surfactant inhibition that consists in the extraction of phospholipid molecules from surfactant membranes by β-D-glucan. Surfactant preparations containing surfactant protein A (SP-A) were more resistant to β-D-glucan inhibition, which reinforces the use of this protein in surfactant replacement therapy.